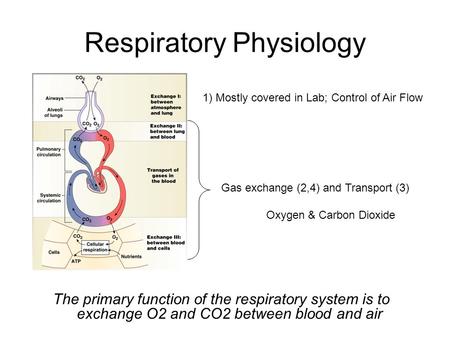
Describe Gas Exchange in the Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
Blood delivery to systemic body tissue delivery of O2 uptake of CO2. CIRCULATION AND GAS EXCHANGE 4.

Pin On Biol O Gee R A P Animated Science Music Videos
The barrier itself is made up of one cell epithelial layer of both pulmonary capillary and the alveolar wall.

. Gas exchange occurs at two sites in the body. Oxygen-poor blood pumped out of the hearts right ventricle travels through the pulmonary circuit. In the lungs carbon dioxide in the blood is exchanged for oxygen at lung alveoli.
Right atrium of the heart receives the deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body through inferior vena cava and deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body is received through superior vena cava. Gaseous exchange happens in the. Pulmonary ventilation provides air to the alveoli for this gas exchange process.
Answer 3Gas exchange takes place in the millions of alveoli in the lungs and the capillaries that envelop them. Discuss the forces involved in the exchange of materials between capillaries and the interstitial fluid. Up to 10 cash back Blood is oxygenated and returned to the left artium via the pulmonary veins.
Start studying Heart as Pump in the Systemic and Pulmonary Circuits. Where is blood oxygenateddeoxygenated as for lab exam. Alveoli are small air sacs that are coated with a moist film that dissolves air.
As shown below inhaled oxygen moves from the alveoli to the blood in the capillaries and carbon dioxide moves from the blood in the capillaries to the air in the alveoli. Gas exchange occurs down a pressure gradient via a. Chapter 42 Circulation and Gas Exchange 621 Blood flows through a pulmocutaneous circuit to the lungs and skin and a systemic circuit to all other organs in a scheme called double circulation.
The purpose of the respiratory system is to perform gas exchange. Pulmonary circulation transports oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle to the lungs where blood picks up a new blood supply. Ventricle lungs and skin to become oxygenated left atrium ventricle all other organs right atrium.
It is also referred to as external respiration as it involves the respiratory processes that have contact with the external environment. Key Areas Covered 1. The now oxygen-rich blood is transported back to the heart by the pulmonary veins.
The process of pulmonary gas exchange removes CO 2 from the blood and replenishes the bloods O 2 supply. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The pump for the pulmonary circuit which circulates blood through the lungs is the right ventricle.
The blood vessels that carry blood to and from the lungs gas exchange Describe the role of the systemic circuit the blood vessels that carry blood to and from all body tissues nutrient and waste exchange Name the three vessels that deliver oxygen-poor blood to the right atrium superior vena cava inferior vena cava and coronary sinus. Systemic circulation flows through arteries then arterioles then capillaries where gas exchange occurs to tissues. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lungsIn the lungs the blood is oxygenated and returned to the left atrium to complete the circuit.
The left ventricle is the pump for the systemic circuit which provides the blood supply for the tissue cells of the body. External respiration is the exchange of gases with the external environment and occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates.
Terms in this set 18 Define and distinguish between pulmonary and systemic circuits Pulmonary - carries blood to lungs for gas exchange. Oxygen-rich blood pumped out of the left ventricle flows through the systemic circuit. Describe the evolution of separate pulmonary and systemic circuits in vertebrates.
Naol alam Advertisement Advertisement New questions in Science. The left ventricle then pumps the oxygenated blood to the body exiting the heart through the aorta. As a result gases can diffuse across the thin endothelium of the alveoli sacs.
The other division of the circulatory system is the. As it passes through the lung the blood gives off carbon dioxide and binds up oxygen. Distinguish between the pulmonary and system circuits and state which part of the heart supplies each one.
At the respiratory membrane where the alveolar and capillary walls meet gases move across the membranes with oxygen entering the bloodstream and carbon dioxide exiting. In the lungs where oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide is released at the respiratory membrane and at the tissues where oxygen is released and carbon dioxide is picked up. The pulmonary circuit transports blood to the lungs.
Blood flow pattern. 2The arteries and veins carry blood around the body. There are two distinct but linked circuits in the human circulation called the pulmonary and systemic circuits.
Describe or draw the path of blood through all parts of the mammalian heart and major arteries and veins near the heart in both systemic and pulmonary circuits aorta pulmonary arteries and veins superior inferior vena cava. Compare extrinsic and intrinsic regulation of cardiac function. The process of gas exchange in which the blood gets oxygenated occurs across a two cell-barrier with the barrier formed between alveoli and pulmonary capillaries.
The pulmonary circuit transports blood to and from the lungs where it picks up oxygen and delivers carbon dioxide for exhalation. Pulmonary gas exchange takes place in the lungs between the alveoli and the blood. Blood delivery to lungs for gas exchange eliminate CO2 uptake O2 describe the systemic circuit.
It then returns to the heart at the left atrium. Compare and contrast the structure and function of mammalian arteries veins and capillaries. The main difference between pulmonary and systematic circulation is that pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs and oxygenated blood back to the heart whereas systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the heart throughout the body and deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Right side of heart. They send oxygen and nutrients to the body tissues. -Right side supplies pulmonary circuit which carries blood to lungs for gas exchange -Left side supplies systemic circuit which carries blood to all organs of the body including lungs and the wall of heart itself.
The blood is oxygenated there and then carried back to the heart. System - supplies blood to all organs left side of heart Describe the general location size and shape of the heart located in the medistinum base - broad superior end. Pulmonary circulation is a low-pressure and high-flow system to play the role of respiratory gas exchange.
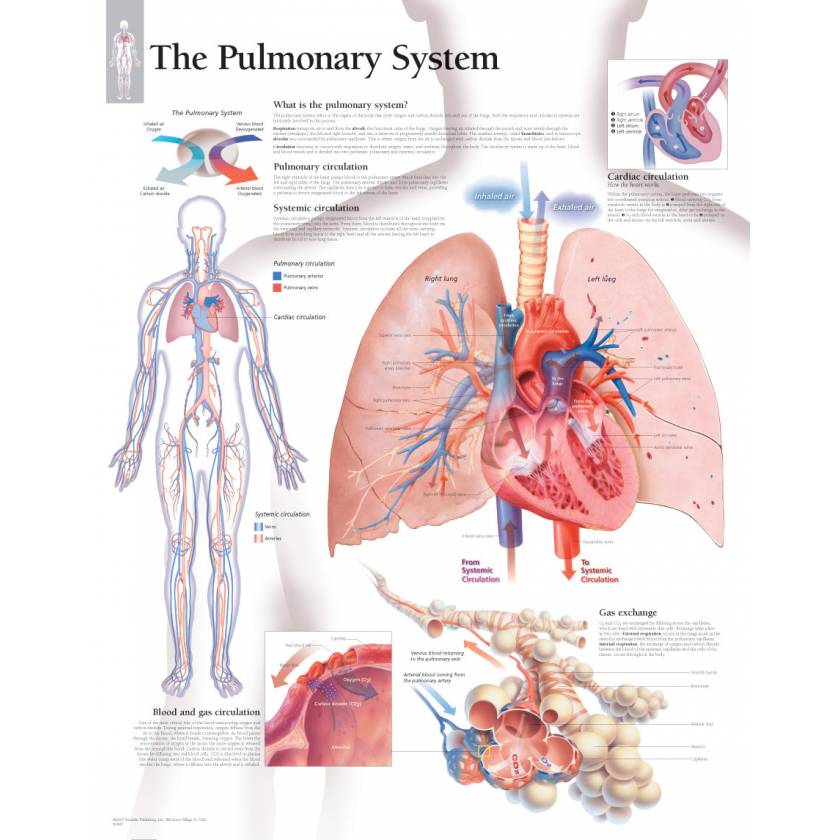
Scientific Publishing The Pulmonary System Chart

The Pulmonary And Systemic Circuits Ppt Video Online Download

Pulmonary And Systemic Circulations Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation

Pulmonary Vein The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Pin En Chapter 22 Respiratory System
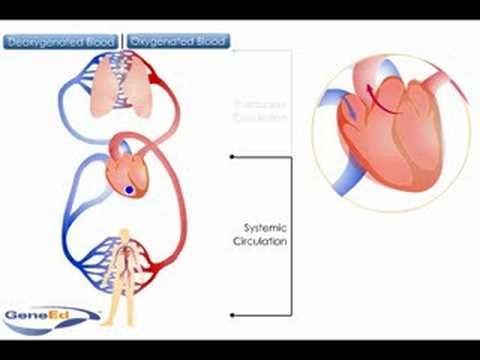
Systemic And Pulmonary Circulation Youtube
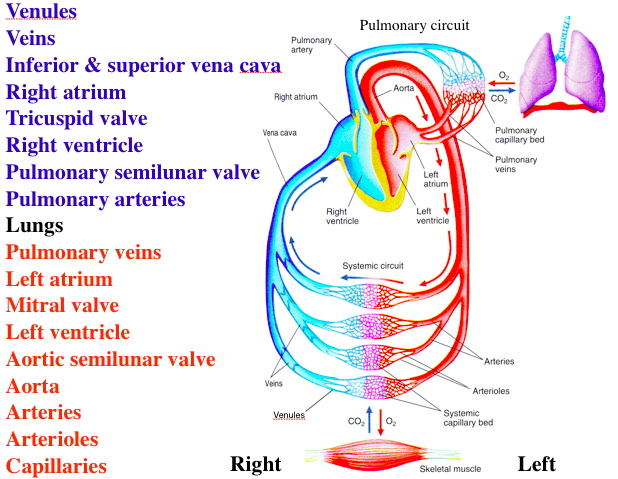
Blood Flow Through Systemic And Pulmonary Circuits
Aabbio The World S Leading Immunotechnology Research And Development Laboratory

Pulmonary And Systemic Circulations Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation

Bio121 Systemic And Pulmonary Circulations Flashcards Quizlet

Systemic Vs Pulmonary Circulation Circulation Youtube

Pulmonary And Systemic Circulation Hsc Pdhpe
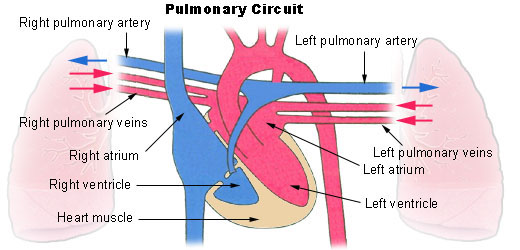
Seer Training Circulatory Pathways

Pulmonary And Systemic Circuit Diagram Quizlet
Despite Having The Same Total Flow Why Is Pressure In The Pulmonary Circulation Lower Than Systematic Circulation Quora

Systemic And Pulmonary Gas Exchange Youtube
The Pulmonary System Chp 16 Ventilation Chp 17 Respiration Ppt Download

Comments
Post a Comment